How to Choose the Right Rapid Shutdown for Your Power Plant
Date: 2022-04-18With the deepening of the transformation of the global energy structure, the new power system with new energy as the main body has become more and more extensive, and more and more buildings have installed photovoltaic systems on the roof. It is foreseen that the installed capacity of photovoltaics will increase on a large scale, whether it is a household system or an industrial and commercial power station, and the safety issues related to it have always attracted the attention of the industry.

In 2010, there was a fire on the photovoltaic roof of residents in Schweringsdorf, Germany, in 2015, on the photovoltaic roof of Apple in Arizona.And in June 2018, the Tesla solar system caught fire in the Amazon warehouse in Redlands, California. As of August 2019 In the past 11 months,the photovoltaic power station on the roof of 7 shopping centers in the United States caught fire and so on. Out of consideration for the safety of people's lives and property, governments around the world have begun to issue safety regulations and policies to minimize the probability of photovoltaic roof fires.

Regarding the safety of photovoltaic systems, the regulatory requirements of countries around the world are not the same. For photovoltaic systems installed on buildings, some countries and regions have issued relevant standards to implement rapid shutdown requirements. In the event of a short circuit and other faults, the DC side high voltage can be quickly cut off through the RSD device (Rapid Shutdown Device), thereby avoiding further the failure is expanded, and the system safety is significantly improved.
Since the regulations for rapid shutdown are not popular in the world, only some countries have issued relevant requirements, and many users have unclear requirements for regulations. NEC regulations, UL1741, UL3741, sunspec protocols... What do these mean? And what are the different requirements between the various regulations? Follow Projoy Classroom today to learn about it!
2014 NEC
The concept of rapid shutdown of photovoltaic systems is proposed by the National Electrical Code (NEC for short). As early as 2014, the NEC2014 690.12<Component-level Self-Shutdown Solution> standard was released, which required the rapid shutdown of photovoltaic systems:
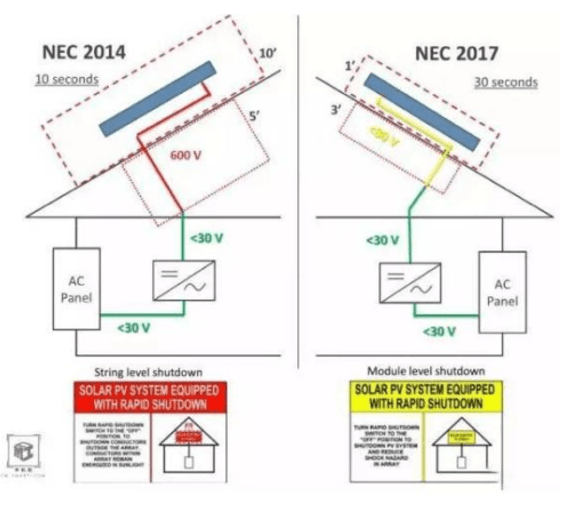
All PV systems on buildings should be installed with rapid shutdown, and the PV system voltage needs to drop below 30V within 10s.
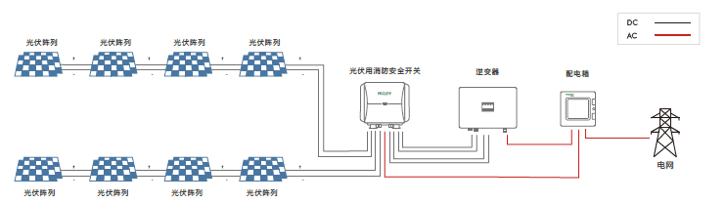
However, this standard rapid shutdown solution only requires the installation of a string-level rapid shutdown device at the access end of the module array, and does not achieve module-level shutdown. There is still a DC high voltage on the roof (in the photovoltaic array).
2017 NEC
On January 1, 2019, Section 690.12(B)(2) of the 2017 NEC <National Electrical Code> on "requirements for rapid shutdown of photovoltaics in photovoltaic arrays" came into effect, and the 2017 NEC regulations required all photovoltaic Facilities are equipped with the ability to achieve component-level rapid shutdown in emergency situations.
The 2017 NEC regulations are based on the 2014 NEC regulations, and have made more stringent requirements for rapid shutdown:
——With the distance to the photovoltaic matrix 305mm as the limit, within 30s after the rapid shutdown device is started, the voltage outside the limit range is reduced to below 30V, and the voltage within the boundary range is reduced to below 80V to achieve module-level shutdown.
The voltage drops to 80V within 30s to meet the basic safety requirements for human contact.
——Install a Listed or field-tagged rapid shutdown system.
<Source: National Electric NEC official website, New Era Securities Research Institute>
Sunspec protocol ≠ fast shutdown certification
A point that needs to be supplemented, the certification (listing) required by NEC refers to the rapid shutdown listing.
Some photovoltaic system sites may see photovoltaic equipment with SunSpec rapid shutdown mark and/or certification. At present, many inverters or some shutdown equipment manufacturers are also promoting SunSpec certification. Users can easily think that having SunSpec means that they are compliant rapid shutdown requirements.
But SunSpec has only developed the important protocol for communication between different devices during rapid shutdown, which is a communication (shutdown) protocol certification. Sunspec certification alone does not satisfy operational aspects or NEC listing requirements in NEC Section 690.12. Sunspec ratings, markings and/or approvals are not a substitute for UL1741 PV Rapid Shutdown Approval (list).

UL1741
As an option in 2017 NEC Section 690.12(B)(2)(1), it is required that within the array boundaries, photovoltaic (PV) arrays shall be certified (listed) or marked as rapid shutdown PV arrays, and PV arrays shall be Install and use in accordance with the instructions included in the Rapid Shutoff PV Array Certification (Listed) or on-site label.
At present, the certification (listing) of photovoltaic systems all implement UL1741 certification requirements. On December 22, 2017, the second edition of UL1741 (for inverters, converters, controllers and interconnection system equipment for distributed a revision of the Safety Standard, which requires extensive evaluation of PV Rapid Shutdown System Equipment and PV Rapid Shutdown Systems.
At the same time, in order to improve the reliability of these safety systems, UL1741 is tested under harsh conditions including hardware failure, software failure, and evaluated under environmental and electrical extreme conditions. PV modules that meet these requirements can be certified (listed) under the UL product categories AC Modules and PV Modules with Integrated Electronics (QHYZ), including Rapid Shutdown.

<Projoy rapid shutdown passed the UL1741 standard test and obtained the North American ETL Certification>
At present, most photovoltaic systems still use centralized or string inverters, which do not have the module-level rapid shutdown function. Therefore, more solutions in the industry are to install module-level rapid shutdown products for the entire photovoltaic system. And more implementation is also UL1741 certification.
UL3741
The new standard requires a "photovoltaic hazard control system" in the photovoltaic system, so that the photovoltaic system in a critical situation is a controllable state.Implement component-level shutdown, within 30 seconds after the rapid shutdown start, the voltage within the boundary range is reduced to below 80V.
UL 3741: The Safety Standard for Photovoltaic Hazard Control was first published in December 2020.
A photovoltaic hazard control system may consist of a single device or a group of devices from one or more manufacturers. The system can consist of PV modules, junction boxes, wiring harnesses,brackets,rapid shutdowns, inverters and other equipment. This standard provides a method to evaluate the operation of photovoltaic system hazard control functions, further reducing the electric shock hazard level of photovoltaic system equipment.
When a PV array consists of a set of equipment, the PV Hazard Control System Installation Instructions and separate QIJR certification will include a list of the equipment required to make up the complete system.
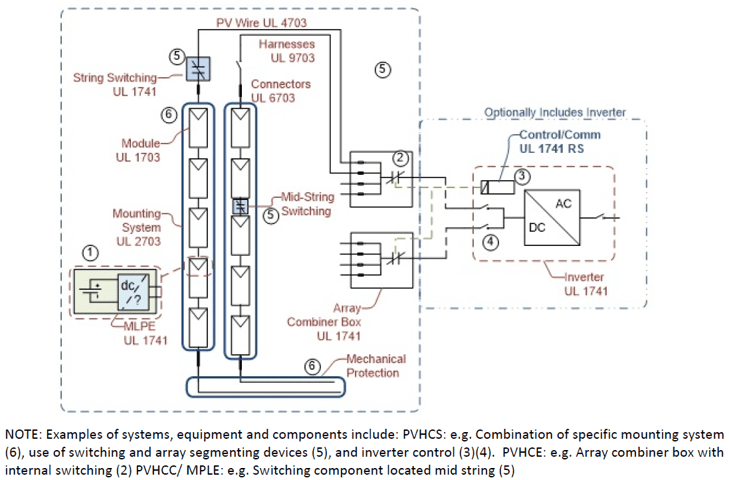
<UL3741 Photovoltaic Hazard Control System Function Diagram>
There is no doubt that countries are paying more and more attention to the safety of photovoltaic systems, and relevant regulations are constantly being upgraded. UL3741 has not been implemented on a large scale, but it is foreseeable that in the future, more products will also follow UL 3741: Photovoltaic Hazard Control Safety standards to be certified.
Extended product
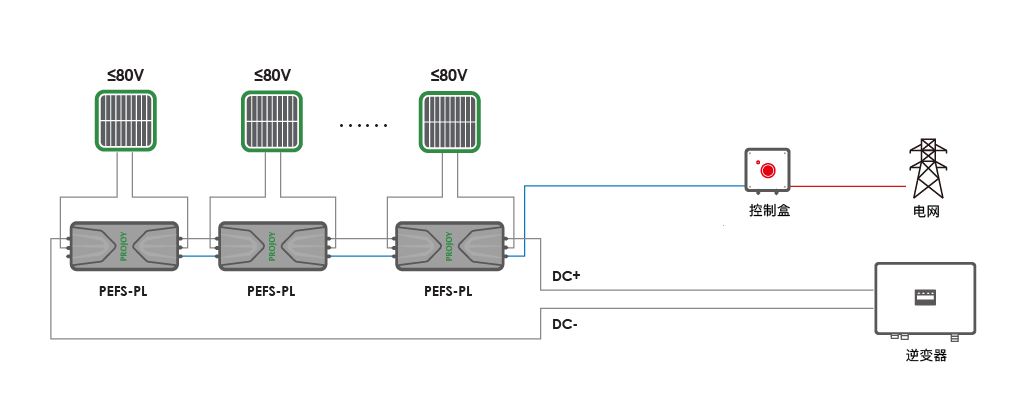
Projoy PEFS-PL series module-level rapid shutdown, each rapid shutdown serves 1 or 2 modules, so that each module is in an open-circuit state, and the voltage between modules will be lower than 80V or the customized voltage range. Meets NEC 2017&2020(690.12) requirements, meets SunSpec certification requirements, and has remote or manual shutdown.
<Projoy PEFS-PL series component level rapid shutdown & control box>
●Built-in temperature sensor, when the temperature exceeds 85 ℃, the device can be automatically cut off.
●In the event of an emergency, the components can be quickly shut down through AC brakes.
●Quick shutdown of components can also be achieved through a rapid shutdown button.
●It can also be switched off manually via the DC switch on the SunSpec inverter.